Healthcare vendor risk management: using CLM to control vendor and service agreements
Healthcare vendor risk management brings contract governance and third-party risk oversight together to protect patient data, ensure regulatory compliance, and prevent disruptions to hospital operations and patient care. Many organizations face challenges coordinating security reviews, ongoing vendor monitoring, and regulatory obligations. Unifying these efforts with contract lifecycle management (CLM) helps address healthcare-specific risks and drives better operational efficiency.
In this article, we’ll cover:
- The link between CLM and healthcare vendor risk management
- Key elements of a robust contract-based vendor risk framework
- Practical technology and automation benefits
- How to address unique risk factors in healthcare contract management
The integration of CLM and vendor risk management
Instead of treating contracts as isolated paperwork, CLM for healthcare centralizes contract terms, vendor risk profiles, compliance documentation, and financial data within a single system. This integration embeds structured risk oversight throughout the entire vendor lifecycle, which is critical under stringent regulatory frameworks such as the GDPR, the NIS2 Directive, the Data Governance Act (DGA), the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), and national healthcare laws.
For example, under NIS2, organizations must implement supply chain and third-party risk management measures, including due diligence, contractual breach notification requirements, and ongoing monitoring of supplier security practices.
Pre-onboarding risk assessments directly inform contract provisions, ensuring that data protection, security requirements, audit rights, liability clauses, and service levels reflect each vendor’s risk profile. After signature, compliance documentation, certifications, and monitoring activities remain linked to the contract record, transforming it into a living control mechanism rather than an archived file.
Core components of a vendor risk management framework
A solid healthcare vendor risk management program within CLM includes:
- Risk assessments: Review vendor security, certifications, and past incidents before onboarding.
- Compliance tracking: Monitor adherence to rules like GDPR, NIS2, and DGA.
- Vendor performance monitoring: Track service quality and contract requirements.
- Incident response planning: Define clear protocols for vendor-related data breaches or disruptions.
- Continuous monitoring: Use real-time tools to spot risks and confirm compliance, not just annual check-ins.
These elements align with European third-party risk management guidance grounded in GDPR, NIS2, DGA, and DORA, which emphasize due diligence, binding contractual safeguards, confidentiality protections, and controlled access to sensitive data.
Through contract management platforms, teams manage obligation tracking, performance milestones, and renewals in searchable repositories, with key milestones, such as expiration dates, renewals, and scheduled risk reassessments, monitored automatically. This reduces gaps and improves hospital operational efficiency.
Technology and automation benefits
CLM for healthcare improves risk management in measurable ways:
- Automated tracking and reminders: Ensure teams never miss compliance deadlines, renewals, or audits.
- Centralized contract repositories: Keep terms, vendor risk data, and spend records in one system to prevent silos.
- Intelligent contract analysis: AI-powered review flags risky language and compliance gaps before and after signing.
- Seamless integration: Connect risk assessment, selection, contracting, and monitoring for smoother operations.
Centralizing contract and risk data reduces the manual effort and helps hospitals respond to audits or disruptions quickly, helping maintain trust with patients and regulators.
Addressing healthcare-specific risk factors
Healthcare vendors introduce risks that go beyond standard commercial concerns. Compensation structures in provider agreements can trigger exposure under fraud statutes. Supply contracts that lack robust business continuity and contingency provisions can jeopardize patient care during disruptions. In payer agreements, unclear termination or notice clauses may interrupt reimbursement flows with little warning.
CLM platforms mitigate these risks by embedding regulatory requirements directly into structured contract playbooks. Standardized clauses, approval workflows, and risk-based templates aligned with applicable frameworks help hospitals reduce drafting errors, enforce compliance, and strengthen their overall risk posture.
Most healthcare organizations evolve progressively: from ad hoc contract tracking to centralized dashboards, then to automated workflows, and ultimately to integration with procurement, financial, and clinical systems. Each stage increases visibility, consistency, and control. In mature programs, vendor contracts are treated as core instruments of vendor risk management, not just procurement documents.
Read next: 10 best contract management software in 2026
🔑 Key takeaways
- Organizations that integrate contract governance with risk oversight are better positioned to reduce compliance failures and minimize operational disruption to patient care.
- Automated tracking, centralized repositories, and AI analysis reduce risk and administrative workload.
- Tailored contract terms and contract playbooks aligned to healthcare regulations address industry-specific vulnerabilities.
- Organizations mature their risk management posture as they move from ad hoc to fully automated and integrated CLM processes.
FAQs
Integrating CLM with vendor risk management connects contract terms, risk profiles, and compliance data in one platform. This ensures that risk assessments shape contract terms from the start, and ongoing monitoring is tied directly to each vendor, improving oversight and reducing administrative effort.
Continuous monitoring helps identify risks in real time instead of relying on periodic checks. This approach ensures ongoing compliance, supports swift responses to issues, and keeps hospitals better protected against emerging threats or changes in regulations.
Healthcare contracts may present unique risks such as violating fraud statutes through certain compensation structures, lacking business continuity provisions in supply contracts, or having vague termination clauses in payer agreements. Addressing these risks requires detailed contract terms aligned with industry regulations.
Best practices include thorough due diligence on vendors, drafting contracts with clear security and compliance requirements, leveraging automation for monitoring, assessing risks throughout the supply chain, and involving cross-functional teams in governance to ensure all perspectives are considered.
Automation in CLM improves risk management by enabling automatic tracking of deadlines, compliance requirements, and renewals. It reduces manual errors, ensures timely action on obligations, and supports faster responses to audits or disruptions, all of which help prevent compliance failures.
Compare European CLM leaders
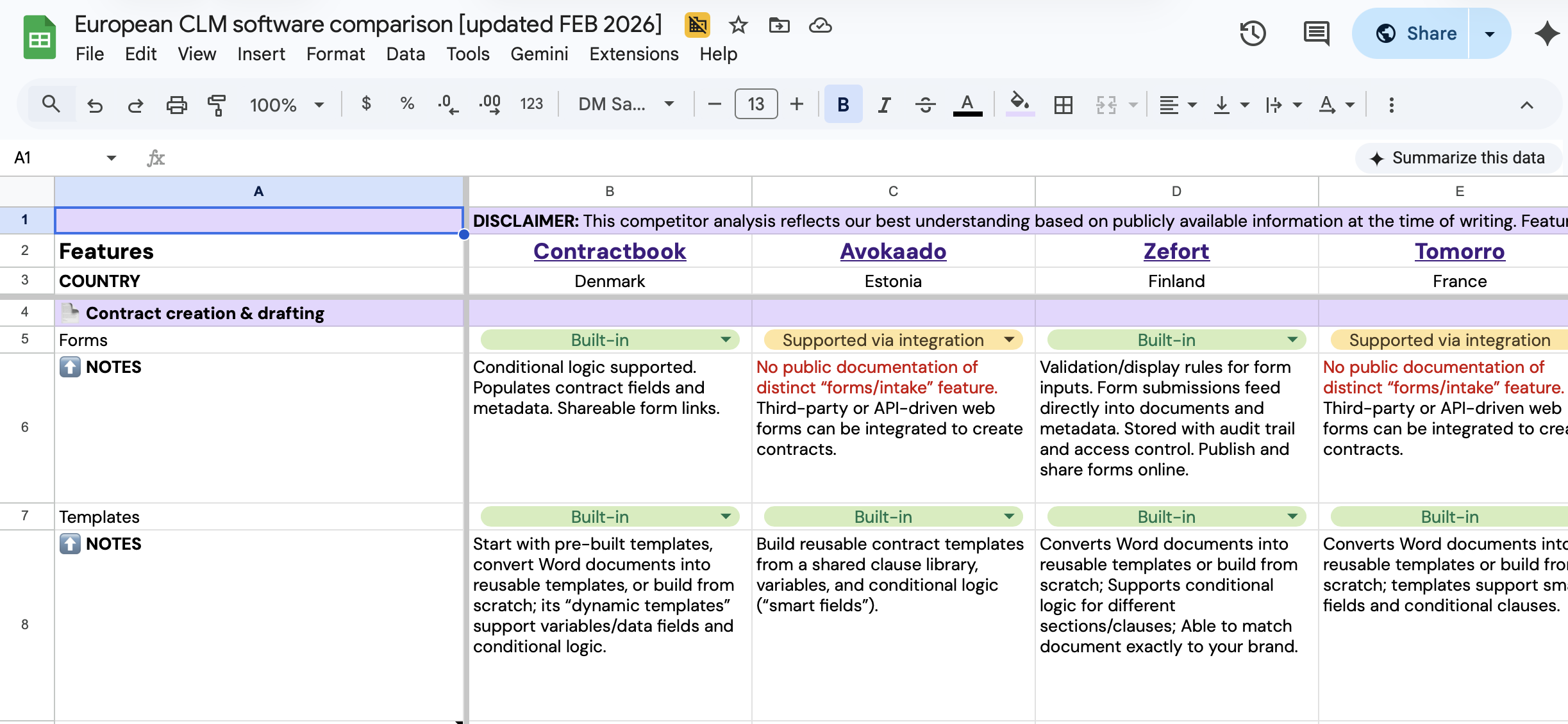
Get a comprehensive breakdown of the top CLM solutions in one spreadsheet.
Compare European CLM leaders

Get a comprehensive breakdown of the top CLM solutions in one spreadsheet.




