CLM implementation: how to successfully implement a CLM system
Successful CLM implementation, especially in highly regulated industries, requires more than just the right tool. It demands a structured, phased approach that addresses compliance, complex workflows, and change management. By breaking the implementation down into clear steps and accountabilities, you can minimize disruptions, secure buy-in, and ensure measurable returns.
Key areas to focus on include:
- How to map and assess your existing contract processes before change
- Which steps to follow for a risk-controlled CLM rollout
- The best practices for regulated industries (compliance, audit trail, data residency)
- Common challenges and clear mitigation strategies
Why structure matters in clm implementation
Regulated environments bring strict documentation, audit, and security standards. Successful CLM implementation relies on a structured project plan, supported by a strong steering committee and a clear product ownership model. This approach keeps priorities on compliance, minimizes business disruption, and delivers value across legal, procurement, and finance teams.
In Deloitte’s experience, organizations with well-defined contract management processes cut cycle times by up to 60% and significantly reduce both financial and compliance risks. This is particularly relevant in the EU, where frameworks like DORA and NIS2 impose high standards for documentation and data hygiene.
10 key steps for successful clm implementation
Implementing CLM effectively requires a well-defined sequence of actions that address both technical and organizational challenges.
1. Understand your contract lifecycle stages
Map each stage: request, creation, negotiation, approval, execution, administration, renewal, and termination. This gives clarity and uncovers process gaps or compliance risks that need addressing.
2. Assess current processes
Audit every workflow and stakeholder. Identify bottlenecks such as manual tracking with spreadsheets or the lack of a single contract repository. Use this as your benchmark for tracking improvement and ROI.
3. Define business requirements
List needs relevant to your business, such as automated approvals, obligation tracking, standardized playbooks, and integration with ERP/CRM. Include requirements for audit trails, granular role-based access, and if relevant data residency (in the EU).
4. Select and configure CLM software
Choose systems with granular role-based access, searchable repositories (with high accuracy), audit trails and immutable logs, and if relevant data residency (in the EU). Prioritize products that can be easily configured, so teams can map responsibilities clearly and adapt the process to whatever rules their industry has to follow.
5. Develop a data migration strategy
Legacy contract data often creates the biggest headache. Cleanse, prioritize (focus on active or high-value contracts first), and validate. Build extra time for complex data hygiene work.
6. Standardize templates and processes
Centralize pre-approved templates and contract clauses. This reduces drafting and negotiation friction, while also slashing financial and compliance risks through enforced policy adherence and comprehensive audit trails.
7. Define roles, responsibilities, and workflows
Assign clear ownership for every phase using models like RACI matrices (see high-level example below). Automate escalations, reminders, and reporting for accountability and efficiency.
| Activity | Legal | IT | Compliance /Risk |
Business |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process and workflow design | R | C | C | C |
| Templates, clause library, playbooks | R | C | C | C |
| Vendor security and architecture | C | R | C | I |
| Regulatory control design | R | C | R | I |
| Integrations and SSO | C | R | I | I |
| Change management & training | R | C | C | R |
| KPIs and reporting definition | R | C | C | C |
R = Responsible, C = Consulted, I = Informed.
8. Pilot and test
Roll out with a select group of high-impact contracts. Test real scenarios, such as amendments, renewals, reporting. Adjust workflows based on user and compliance feedback.
9. Train users and roll out
Deliver targeted, role-centered training. Assign internal champions. Embed CLM skills into onboarding and support ongoing learning for process adoption.
10. Monitor, measure, and optimize
Use dashboards to track KPIs: cycle time, renewal rates, compliance, cost savings (aim for 10–30%), and error reduction. Iterate based on analytics and regular feedback.
Best practices for regulated industries
To maintain compliance and efficiency in high-regulation sectors, use proven methods suited to strict legal and operational frameworks.
- Prioritize compliance and security: Enable automated notifications, version control, and full audit trails. Use encryption and EU-based data residency to meet GDPR or sector rules.
- Foster cross-functional alignment: Involve stakeholders early: legal, procurement, finance, and business units. Treat contracts as managed, strategic assets.
- Leverage AI and automation: Use AI for risk review, clause extraction, and obligation management. Automated processes prevent manual error and reduce operational costs.
- Centralize everything: One secure repository eliminates silos, increases visibility, and supports easier compliance audits.
Common challenges and mitigation strategies
Organizations face recurring hurdles during CLM implementation. These can be addressed with proactive planning and targeted interventions.
| Challenge | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Resistance to change | Secure executive sponsorship and communicate ROI such as faster contract cycles and fewer disputes. Start with a focused pilot. |
| Data quality/migration issues | Cleanse and validate contract data before and after migration. |
| Incomplete adoption | Mandatory role-based training, dashboards, and align KPIs with adoption targets. |
| Overlooking post-go-live | Schedule regular audits, feedback, and use AI tools for performance reports. |
Start iteratively, focusing initial efforts on high-volume or compliance-heavy workflows.
Read next: 10 Best Contract Management Software in 2026 or maybe you need tips for migrating from an existing CLM?
🔑 Key takeaways
- A phased CLM implementation improves adoption, compliance, and long-term ROI.
- Success relies on clean processes, strong steering committee oversight, and well-defined roles (documented via RACI matrix or similar tools).
- Prioritize data migration, user training, and post-launch monitoring for minimal disruption.
- Focus first on compliance-heavy workflows to build momentum and measurable results.
FAQs
Begin by mapping current contract processes and identifying inefficiencies or compliance gaps. Define clear business and compliance requirements. Select and configure software that supports audit trails and security needs. Prioritize careful data migration, train users, launch a pilot, and monitor metrics to continually improve adoption and processes.
Audit and cleanse contract data before migration to ensure accuracy. Focus first on active or high-value contracts. Validate data after migration and allow additional time for addressing legacy data issues, which are common in regulated industries.
Involving key teams like legal, procurement, finance, and business units from the outset helps align on compliance, risk management, and process needs. Early engagement supports buy-in, reduces resistance, and ensures the CLM solution meets all regulatory and operational requirements.
Secure executive sponsorship and communicate the benefits, such as faster contract cycles and fewer errors. Start with a pilot focused on high-impact areas and provide targeted training to support adoption.
Typical issues include resistance to change, data migration difficulties, and incomplete adoption. Tackle these with strong leadership, rigorous data validation, mandatory training, KPI-driven incentives, and post-launch process auditing.
Compare European CLM leaders
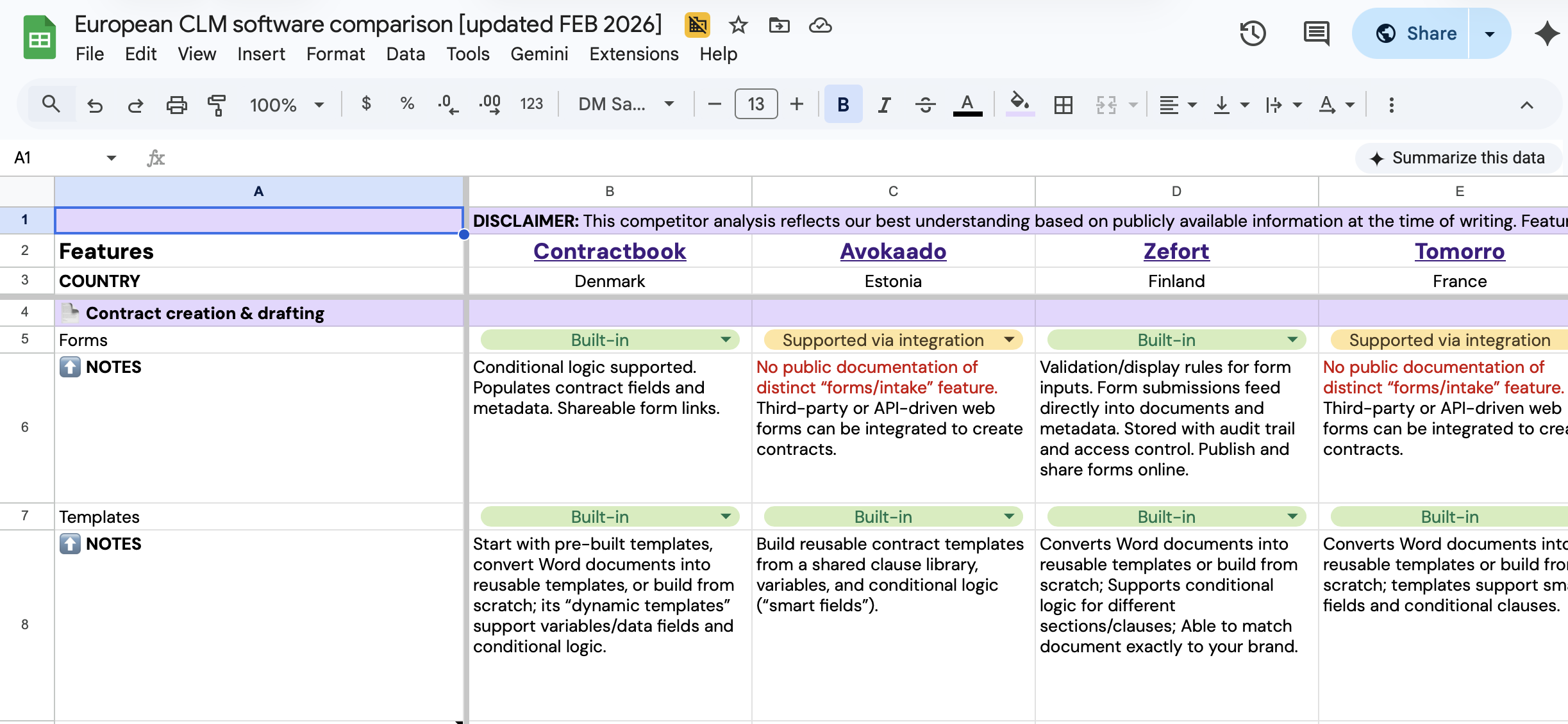
Get a comprehensive breakdown of the top CLM solutions in one spreadsheet.
Compare European CLM leaders

Get a comprehensive breakdown of the top CLM solutions in one spreadsheet.




